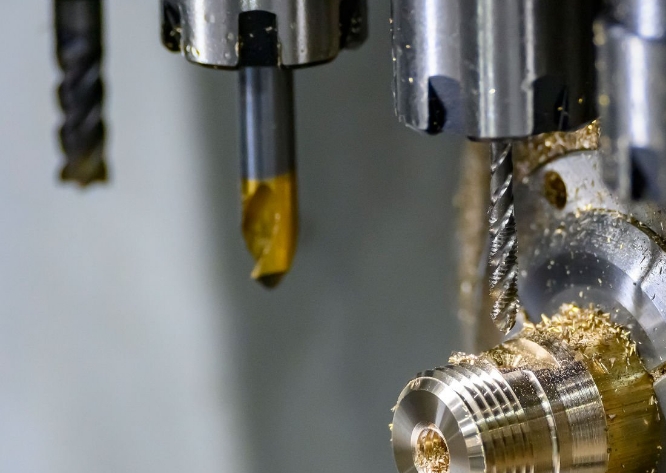
In the realm of modern manufacturing and engineering, machine shops stand as bastions of precision and innovation. These specialized facilities, equipped with an array of advanced machinery and skilled craftsmen, play a pivotal role in shaping raw materials into intricate components that drive industries ranging from aerospace and automotive to medical and electronics.
This article will take you through a comprehensive understanding of the different machinery, functions, and safety protocols in mechanical workshops. Finally, we will also discuss the advantages, applications, and challenges of mechanical workshops, as well as their key roles in various industries.

What is a Machine Shop?
Machine shop, as a term, refers to a facility or workshop where various machining operations are performed on raw materials or semi-finished products to create finished parts, components, or assemblies.
These shops typically house a variety of machine tools and equipment operated by skilled machinists and technicians. These devices are not just simple tools, they represent the latest advances in advanced manufacturing technology and can quickly transform design concepts into actual parts and products. Machine shops can offer services such as CNC machining, milling, turning, drilling, grinding, and fabrication of parts according to precise specifications.
Functions of a Machine Shop:
- Production of Precision Parts: Machine shops are equipped with highly precise machinery that can create parts with tight tolerances and high accuracy. This precision is crucial in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing.
- Customization and Modification: Machine shops have the capability to customize and modify existing parts or components to meet specific requirements. This flexibility allows for the adaptation of standard parts to unique applications.
- Repair and Maintenance: In addition to producing new parts, machine shops also provide repair and maintenance services for worn-out or damaged components. This ensures the continued operation of critical equipment and machinery.
- Prototyping and Development: Machine shops play a vital role in the development of new products and technologies. They can quickly produce prototypes and test iterations, allowing for rapid iteration and refinement of designs.
History of Machine Shops
Machine shops have evolved significantly over time, starting from manual operations in the 19th century to the introduction of CNC technology in the 20th century, and now incorporating advanced automation, AI, and robotics in the 21st century. These advancements have revolutionized manufacturing, enhancing precision, efficiency, and the complexity of parts produced.
The Importance of Machine Shops
Machine shops play a crucial role in the manufacturing industry, as they enable the production of complex parts and components that are essential for a wide range of products and applications. From automotive components to aerospace parts, medical devices, and more, machine shops provide the precision and accuracy necessary to meet demanding specifications.
Types of Machine Shops
There are several types of machine shops, including job shops, contract shops, and captive shops. Job shops typically accept a variety of jobs from different customers, while contract shops specialize in fulfilling long-term contracts with specific customers. Captive shops, on the other hand, are owned by a larger company and primarily serve the needs of that company.
What Does a Machine Shop Do?
A machine shop specializes in manufacturing and modifying parts and components from various materials such as metal, plastic, and composite materials. They utilize a range of machine tools and equipment to perform operations like cutting, shaping, drilling, milling, turning, grinding, and finishing.
Machine shops cater to industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, medical devices, and more, producing custom parts according to precise specifications provided by clients or engineers. They play a crucial role in prototype development, production of replacement parts, and creating components essential for machinery and equipment used across different sectors.
Structure and Machinery of a Machine Shop
A machine shop is a facility that specializes in the manufacturing and assembly of precision machine parts and components. It is a critical component in the industrial sector, as it enables the production of tools, equipment, and devices that are essential for various industries.
Structure of a Machine Shop
The structure of a machine shop typically consists of several key areas:
- Workshop Area: This is the main area where the majority of the machining operations are performed. It is equipped with various types of machine tools, such as lathes, milling machines, drills, and grinding machines.
- Storage Area: This area is used to store raw materials, finished products, and tools. It is important to maintain an organized storage system to ensure efficient workflow.
- Inspection Area: This area is dedicated to quality control and inspection. It is equipped with precision measuring instruments and equipment to ensure that the manufactured parts meet the required specifications.
- Office Area: The office area is where administrative tasks, such as order processing, inventory management, and accounting, are performed.
- Support Facilities: This includes areas for tool sharpening, maintenance, and repair of machinery. Additionally, there may be facilities for staff training and development.
Machinery in a Machine Shop
The machinery in a machine shop varies depending on the specific requirements and capabilities of the shop. However, some common types of machinery include:
- Lathes: Lathes are used to rotate a workpiece and perform various cutting operations, such as turning, facing, and threading. To learn more about lathes, please read this article: What is a Lathes?
- Milling Machines: Milling machines are used to remove material from a workpiece by rotating a cutter against it. They can be used to create complex shapes and contours.
- Drills: Drills are used to create holes in a workpiece. They can be manual or powered by an electric motor.
- Grinding Machines: Grinding machines are used to finish the surface of a workpiece by abrasion with a rotating wheel. They are commonly used for precision grinding and polishing.
- Presses: Presses are used to apply force to a workpiece to deform or cut it. They can be used for forging, stamping, and other metalworking operations.
In addition to these common machines, a machine shop may also have specialized equipment for specific applications, such as CNC (CNC stand for Computer Numerical Control) machines, wire EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) machines, and laser cutting machines.
Housekeeping and Recycling Practices in Machine Shops
Housekeeping
- Organized Shops:
- Shops are swept clean before the end of every shift.
- Equipment care and maintenance are prioritized.
- Swarf (chips) produced during machining is removed daily.
- Machines are air-blown and wiped clean regularly.
- Less Organized Shops:
- No fixed schedule or routine for sweeping and cleaning.
- Chips may be left in machines until their removal is absolutely necessary.
- Infrequent cleaning can lead to operational inefficiencies and potential equipment damage.
Recycling
- Active Recycling Shops:
- Residual materials like aluminum, steel, and oil are collected and recycled.
- Recycled materials are often sold for additional revenue.
- Dedicated personnel or departments (e.g., HSEQ) enforce recycling protocols.
- Proper separation and storage of recyclable materials are maintained.
- Less Active Recycling Shops:
- Not all shops practice recycling consistently.
- Lack of personnel dedicated to enforcing recycling habits.
- Potentially miss out on environmental and financial benefits.
Operations in a Machine Shop
Machining Processes
Turning
Turning is a machining process where a workpiece is rotated on a lathe while a cutting tool is fed against it to remove material and create a desired shape. This process is commonly used to produce cylindrical parts such as shafts, rods, and other components with round cross-sections.
Milling
Milling involves the use of a rotating cutter (milling cutter) to remove material from a workpiece. It is a versatile process that can be used to create complex shapes, contours, and features on parts. Milling machines are capable of performing various operations, including planar milling, contouring, drilling, and threading.
Drilling
Drilling is a machining process where a rotating drill bit is used to create holes in a workpiece. This process is essential for numerous applications, such as installing fasteners, creating passages for fluids or gases, and machining precision holes for components.
Grinding
Grinding is a precision machining process that utilizes abrasive wheels or discs to remove small amounts of material from a workpiece. It is commonly used to achieve high surface finishes, tight tolerances, and complex shapes that require precise dimensional control. Grinding is often a finishing operation performed after other machining processes.
Equipment and Tools
Machine shops rely on a wide range of equipment and tools to perform various machining operations. This includes metalworking machines such as lathes, milling machines, drilling machines, and grinding machines. Additionally, precision measuring instruments like micrometers, calipers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) are used to ensure accuracy and quality.
Cutting tools, such as drills, end mills, turning tools, and grinding wheels, are essential for removing material from workpieces. Fixtures and workholding devices, like vices, chucks, and clamping systems, are used to securely hold workpieces in place during machining operations.
The specific equipment and tools used in a machine shop depend on the types of parts being produced, the required level of precision, and the available resources.
Quality Control
Quality control is a fundamental aspect of machine shop operations. It involves the implementation of inspection methods and tools to ensure that parts meet the specified requirements, dimensions, and tolerances. Quality control ensures that the final product meets the customer’s expectations and adheres to industry standards.
Inspection methods may include dimensional inspections using precision measuring instruments, surface finish measurements, material testing, and other techniques. Non-destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection, may also be employed to detect internal defects or discontinuities in parts.
Quality control procedures are typically implemented throughout the machining process, from raw material inspection to final inspection before shipment. Any issues or deviations from specifications are identified and corrected promptly to ensure the quality of the final product. Regular maintenance and calibration of equipment and tools are also essential for maintaining consistent quality.
Safety Practices
At the core of safety practices in machine shops lies the importance of training and education. Employees must be thoroughly trained on the operation of machinery, safety procedures, and emergency response measures. Regular refresher courses and workshops should be conducted to keep employees updated on the latest safety standards and best practices.
Additionally, the machine shop should have a clear set of safety policies and procedures that are strictly adhered to. These policies should cover areas such as the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), machine maintenance, and housekeeping. PPE, such as safety glasses, gloves, and earplugs, should be worn at all times when operating machinery. Regular machine maintenance is crucial to prevent breakdowns and accidents. Housekeeping, including keeping the workspace clean and organized, is also essential to reduce trip hazards and other potential dangers.
Furthermore, machine shops should conduct regular safety audits and inspections. These audits should assess the compliance of employees with safety policies, the condition of machinery, and the overall safety of the workspace. Any identified hazards or issues should be promptly addressed to prevent accidents.
Role of Machine Shop in Modern Manufacturing
In today’s fast-paced and technology-driven manufacturing environment, machine shops play a crucial role in ensuring the efficiency, quality, and flexibility of the production process. With the advent of advanced technologies such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining, machine shops can now achieve unprecedented levels of precision and productivity.
CNC machining, for example, allows for the programming of complex machining operations directly into the machine tool. This eliminates the need for manual operation and reduces the potential for human error. Furthermore, CNC machines can be easily reprogrammed to produce different parts, providing a high level of flexibility and adaptability.
Manual vs Automated Machining
| Feature | Manual Machining | Automated Machining (CNC) |
|---|---|---|
| Human Intervention | High | Minimal |
| Accuracy & Precision | Lower, dependent on operator skill | High, consistent |
| Number of Operations | Limited, often requires multiple setups | Multiple operations with ATC (Automatic Tool Changer) |
| Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Safety | Lower, more risk of human error and accidents | Higher, reduced human interaction |
| Complexity of Parts | Limited by manual capabilities | Can handle complex geometries |
| Consistency | Variable, operator-dependent | High, machine-controlled |
| Setup Time | Longer | Shorter |
| Flexibility | High for simple, one-off tasks | High for complex, repeatable tasks |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher for low-volume, simple jobs | Higher for high-volume, complex jobs |
How to Select the Right Machine Shop?
When selecting the right machine shop, there are several key factors to consider to ensure you make an informed decision. Here are some steps to follow in the selection process:
- Define Your Needs:
- Clearly identify the type of machining work you require, such as milling, turning, grinding, etc.
- Determine the materials you need to work with, as different machines are suited for different materials.
- Assess the volume and frequency of work to determine if you need a full-service shop or a specialized one.
- Research and Evaluate:
- Research different machine shops in your area or online.
- Check the shops’ websites or catalogs for information on their equipment, capabilities, and services.
- Look for shops that have experience working with your specific materials and applications.
- Consider Quality and Experience:
- Ask for samples or references from previous customers to evaluate the quality of the shop’s work.
- Inquire about the shop’s certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicate a commitment to quality and consistency.
- Consider the shop’s years of experience and reputation in the industry.
- Assess Capabilities:
- Verify that the shop has the necessary equipment to handle your specific requirements.
- Ask about the shop’s maximum workpiece size, material capabilities, and tolerance ranges.
- Determine if the shop can meet your production schedule and delivery requirements.
- Evaluate Cost and Value:
- Request quotes from several shops to compare pricing.
- Consider not only the initial cost but also the overall value, including quality, service, and support.
- Ask about any hidden costs or additional fees that may apply.
- Visit the Shop:
- If possible, arrange a visit to the shop to see the equipment, facility, and staff in person.
- Observe the shop’s organization, cleanliness, and overall atmosphere.
- Ask questions to get a sense of the shop’s culture, communication, and customer service.
- Evaluate Customer Service:
- Consider the shop’s responsiveness to inquiries and quotes.
- Ask about their communication methods and how they handle issues or concerns.
- Determine if they offer after-sales support or maintenance services.
- Make Your Decision:
- Weigh all the factors and choose the shop that best meets your needs, requirements, and budget.
- Remember that the right shop is not just about price but about quality, experience, capabilities, and customer service.
By following these steps and evaluating each shop based on your specific requirements and criteria, you can select the right machine shop for your needs.
Machine Shops in Different Industries
Machine shops serve a variety of industries, providing essential manufacturing services that cater to specific needs and requirements. Here are some industries where machine shops play a crucial role:
| Industry | Role of Machine Shops | Application Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Precision machining and fabrication of engine components, transmission parts, and chassis elements. | Engine blocks, transmission housings, suspension arms |
| Aerospace and Defense | Manufacturing complex, high-tolerance components for aircraft, satellites, and defense systems. | Aircraft wing structures, satellite panels, missile bodies |
| Medical Devices | Producing sterile and biocompatible components with tight tolerances for medical instruments and implants. | Surgical instruments, pacemaker casings, prosthetic joints |
| Electronics and Semiconductors | Precision machining of intricate parts for electronic devices and semiconductor manufacturing equipment. | Microscopic components for circuit boards, semiconductor molds, LED housings |
| Oil and Gas | Fabrication of durable, corrosion-resistant parts for drilling rigs, valves, and pipelines. | Drill bits, pipeline valves, wellhead components |
| Industrial Equipment | Machining large-scale parts and assemblies for heavy machinery used in manufacturing and construction. | Excavator arms, CNC machine bases, industrial conveyor systems |
| Consumer Products | Crafting aesthetic and functional components for household goods, appliances, and recreational equipment. | Kitchen appliance casings, bicycle frames, golf club heads |
| Renewable Energy | Manufacturing components that withstand environmental stresses for wind, solar, and hydroelectric systems. | Wind turbine blades, solar panel mounting brackets, hydro turbine hubs |
| Telecommunications | Producing precise components for communication devices and network infrastructure equipment. | Antenna arrays, fiber optic connectors, satellite communication dishes |
| Food and Beverage | Creating sanitary components for food processing and packaging machinery, ensuring compliance with hygiene standards. | Stainless steel conveyors, food packaging machine parts, bottling line components |
Advantages and Challenges of Machine Shop
Operating a machine shop comes with its own set of advantages and challenges. Here’s a breakdown of both:
Advantages of Machine Shop
- Customization and Flexibility: Machine shops can produce custom parts tailored to specific client requirements, offering flexibility in manufacturing.
- Precision and Quality Control: Advanced machining techniques allow for high precision and quality control, ensuring consistent and accurate parts.
- Versatility in Materials: Machine shops can work with a wide range of materials, from metals like aluminum and steel to plastics and composites.
- Fast Turnaround: With efficient processes and modern equipment, machine shops can often deliver parts quickly, meeting tight deadlines.
- Cost Efficiency: Depending on scale and specialization, machine shops can offer cost-effective solutions compared to in-house manufacturing for complex parts.
- Innovation and Technology: Constant advancements in CNC technology, automation, and CAD/CAM software enable machine shops to stay competitive and innovative.
- Diverse Market Opportunities: Serving various industries like automotive, aerospace, medical, and consumer goods provides diverse market opportunities.
Challenges and Solutions in Machine Shops
Material Handling
Material handling is a common challenge in machine shops, as it involves the efficient movement and storage of raw materials, work-in-process parts, and finished products. Solutions include the use of material handling equipment such as cranes, forklifts, and conveyors, as well as the implementation of lean manufacturing principles to minimize waste and improve efficiency.
Machine Maintenance
Maintaining the equipment and tools in a machine shop is essential for ensuring their reliability and performance. However, machine maintenance can be challenging due to the complexity of the equipment and the demanding work environment. Regular maintenance schedules, trained maintenance personnel, and the use of preventive maintenance techniques can help to address these challenges.
Workforce Development
Finding and retaining skilled workers is another challenge facing machine shops. With the advancement of technology, the need for workers with specialized skills and knowledge has increased. To address this issue, machine shops can invest in training and development programs for their employees, as well as partner with educational institutions to attract new talent.
Choose a Machine Shop Near You
Experience precision and reliability with BOYI expert CNC machining services. Whether you’re in aerospace, automotive, electronics, or any other industry requiring high-quality machined parts, BOYI delivers excellence. Our state-of-the-art facilities and skilled technicians ensure that every component meets your exact specifications.
From prototype to production, trust BOYI for efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover why leading companies choose BOYI for CNC machining solutions.

Let’s Start A New Project Today
Our engineers will contact you within 2 hours.
FAQ
Machine shops offer a range of services including CNC machining, milling, turning, drilling, grinding, and fabrication of precision parts from various materials like metals, plastics, and composites.
Yes, many machine shops offer prototyping services to help clients develop and refine designs before full-scale production. Prototyping allows for testing and validation of parts to ensure they meet functional and performance requirements.
Machine shops can work with a wide range of materials, including metals such as aluminum, steel, titanium, and copper alloys, as well as plastics, composites, and specialty materials based on project requirements.
Ensure the machine shop has stringent quality control processes in place, such as ISO certifications. Ask about their inspection equipment and procedures to ensure parts meet specified tolerances and standards.
Catalog: CNC Machining Guide

This article was written by engineers from the BOYI team. Fuquan Chen is a professional engineer and technical expert with 20 years of experience in rapid prototyping, mold manufacturing, and plastic injection molding.